
In the late twelfth and early thirteenth century there lived a mechanically inclined polymath named Badi’ al-Zaman Abu-‘l-‘Izz Ibn Isma’il Ibn al-Razzaz al-Jazari, whom we might prefer simply to call Al-Jazari. A resident of Diyar-Bakir, in modern-day Turkey, he was employed as a court engineer, and indeed, proved to be the finest engineer for which a Mesopotamian ruler of that era could hope. He worked out a variety of functional camshafts, crankshafts, pumps, fountains, and clocks, not to mention his more ambitious designs, including a host of humanoid automata meant to handle tasks like serving beverages and even playing music.

Lying between the practical and the fanciful are such Al-Jazarian inventions as the “perpetual flute,” a diagram of which you can see at the site of the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Involving “two adjacent tanks, each with a plug attached to a chain,” the setup would work when “the pipe on an axle with a bowl fills with water from a channel at the upper right and tips so that water flows into one tank. The air in the tank is thus forced through a pipe attached to a jar that plays a flute until the tank is filled. Then the pipe tilts to fill the other tank with water, causing the other flute to play.” Like a pre-modern Rube Goldberg, Al-Jazari created mechanical concepts that are better seen than explained, and you’ll find many more of them illustrated at Flashbak.
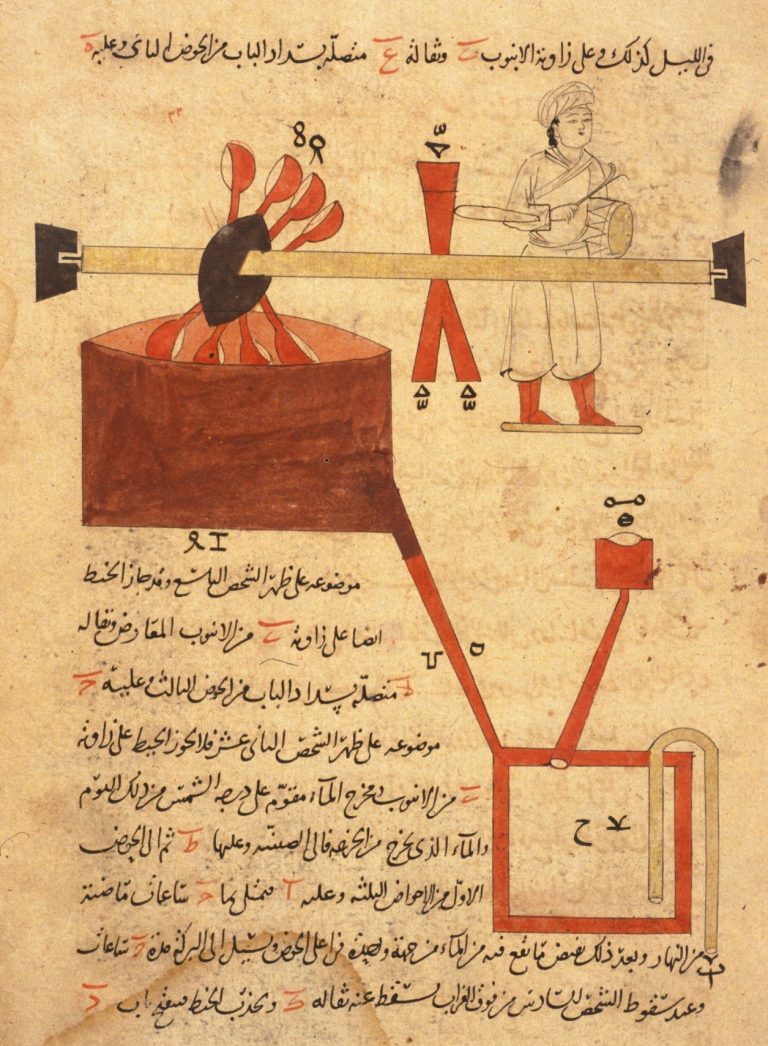
These works of schematic art come not from Al-Jazari’s own hand, but from an Arabic manuscript created some three to six centuries after his death. It appears to pay a kind of tribute to his popular Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices, which itself drew upon a ninth-century Book of Ingenious Devices written by three Persian brothers known as the Banu Musa. All of these artistic and technical works, and their continued availability in different forms through the generations, reflect the serious work of intellectual custodianship and development across the civilizations of the Middle East after the fall of the Roman Empire — a project that greatly benefited from the occasional sui generis imagination like Al-Jazari’s.
If you would like to sign up for Open Culture’s free email newsletter, please find it here. It’s a great way to see our new posts, all bundled in one email, each day.
If you would like to support the mission of Open Culture, consider making a donation to our site. It’s hard to rely 100% on ads, and your contributions will help us continue providing the best free cultural and educational materials to learners everywhere. You can contribute through PayPal, Patreon, and Venmo (@openculture). Thanks!
via Flashbak
Related content:
Download 10,000+ Books in Arabic, All Completely Free, Digitized and Put Online
How Arabic Translators Helped Preserve Greek Philosophy … and the Classical Tradition
500+ Beautiful Manuscripts from the Islamic World Now Digitized & Free to Download
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the Substack newsletter Books on Cities, the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.


So.… it looks like Rube Goldberg was Arab.…
Who knew ??
;)
/s
Satire.… NOT Sarcasm.….
:)
Great story on underestimated scientific contributions of the Arab civilization. Thank you,
I have been interested in Al Jazari for quite a while. I think the purpose of the first mechanism illustrated is not well enough understood. It may have been described as a “whistle”, but the important aspect of this invention is the steady air pressure it provided. This was needed for so many of the industries that were developing all over the middle east that eventually passed on to Europe as the forests of the middle east were destroyed. The only fuel for bronze, iron, steel, glass, and ceramic workshops was charcoal! To obtain the 1000 degrees or so for most of these operations they needed a steady stream of air! This is basically a hydo-bellows with many applications.
The environment went through enormous changes from the discovery of tin and the resulting bronze industry in about 3000 BC (probably in present day Afghanistan) to the collapse of the entire middle eastern economy when Spain started stripping the Americas of gold and silver and dumping them into the new world. It was like printing way too much currency! Eventually the final nail went in the coffin when the Ottoman Sultan, in desperation to raise taxes, taxed the trees!
That is how Europe suddenly took the lead — forests and rivers and mountain streams galore!