We remember Catch-22, more than half a century after its publication, as a rollicking satire of American military culture in wartime. But those of us who return to Joseph Heller’s debut novel, a cult favorite turned bestseller turned pillar of the modern canon, find a much more complex piece of work. Heller began writing the manuscript in 1953, while still employed as a copywriter at a small advertising agency. The project grew in ambition over the next eight years he spent working on it, eventually in collaboration with editor Robert Gottlieb and its other advocates at Simon & Schuster, the publisher that had bought it.
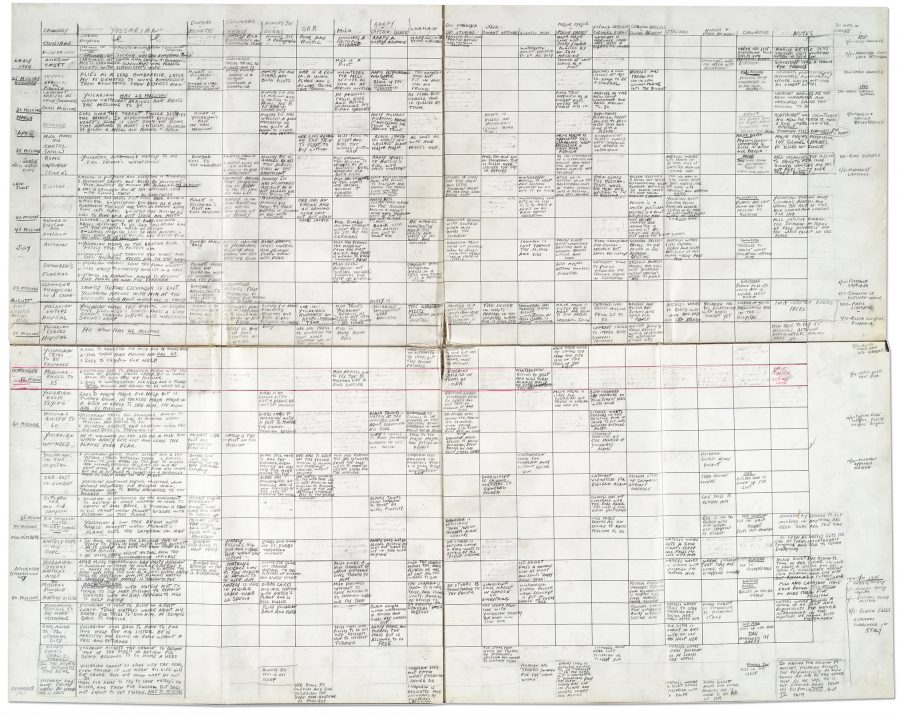
When Catch-22 finally went into print, one of those advocates, an advertising manager named Nina Bourne, launched an aggressive one-woman campaign to get copies into the hands of all the influential readers of the day. “You are mistaken in calling it a novel,” replied Evelyn Waugh. “It is a collection of sketches — often repetitious — totally without structure.” But the book’s apparently free-form narrative, full of and often turning on puns and seemingly far-fetched associations, had actually come as the product of a deceptive compositional rigor. As one piece of evidence we have Heller’s handwritten outline above. (You can also find a more easily legible version here.)
The outline’s grid presents the events of the story in chronological order, as the novel itself certainly doesn’t. The rows of its vertical axis run from early 1944 at the top to December 1944 at the bottom, and the columns of its horizontal axis lists the book’s major characters. They include the protagonist John Yossarian, Air Force bombardier; the “poor and rustic” Orr; Colonel Cathcart, a “Harvard graduate with a cigarette holder,” and Major Major, who “looks like Henry Fonda.” Within this matrix Heller kept track of what should happen to which characters when, at the time of which events of the real war.
The descriptions of events sketched on the outline range from the broadly comic (“Chaplain spies Yossarian naked in a tree and thinks it is a mystical vision”) to the cynical (“Milo justifies bombing the squadron in terms of free enterprise and the large profit he has made”) to the straightforwardly brutal (“Snowden is shot through the middle and dies”). Their placement together in the same neutral space reflects the single quality that, perhaps more than any other, brought upon the novel such a wide range of reactions and earned it a lasting place in not just American literature but American culture. Look at all the aspects of war straight on, it reminds us still today, and the total picture — bloody and senseless for the individual participant, though not without its minor triumphs and laughs — looks something like absurdist art.
Related Content:
Kurt Vonnegut Diagrams the Shape of All Stories in a Master’s Thesis Rejected by U. Chicago
How J.K. Rowling Plotted Harry Potter with a Hand-Drawn Spreadsheet
How Famous Writers — From J.K. Rowling to William Faulkner — Visually Outlined Their Novels
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities and culture. His projects include the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.


One of the most over-rated books in history. Just sayin’
Easily the funniest book I’ve ever read, and yet by the conclusion a sombre mood has descended upon the convoluted narrative.
A masterpiece.