Creative Commons image by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin
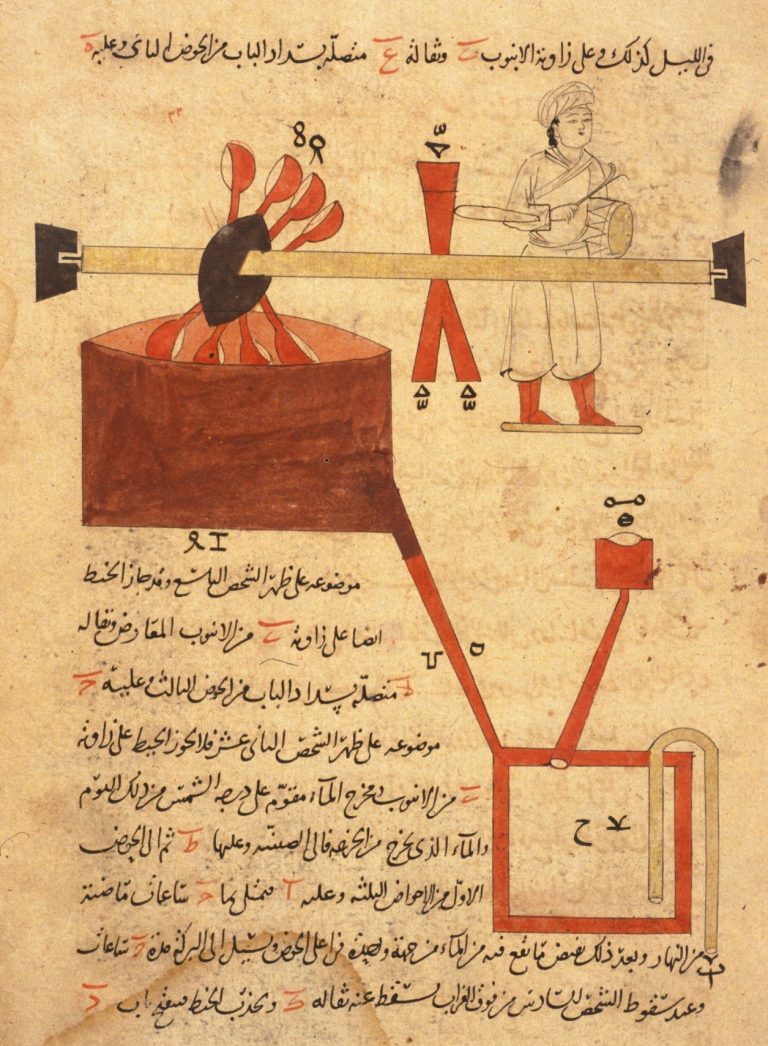
Long ago, in the ancient civilization of Mesopotamia, Akkadian was the dominant language. And, for centuries, it remained the lingua franca in the Ancient Near East. But then it was gradually squeezed out by Aramaic, and it faded into oblivion once Alexander the Great Hellenized (Greekified) the region.
Now, 2,000+ years later, Akkadian is making a small comeback. At Cambridge University, Dr. Martin Worthington, an expert in Babylonian and Assyrian grammar, has started recording readings of poems, myths and other texts in Akkadian, including The Epic of Gilgamesh. This clip gives you a taste of what Gilgamesh, one of the earliest known works of literature, sounds like in its mother tongue. Or, you can jump into the full collection of readings right here, courtesy of the University of London.
If you would like to sign up for Open Culture’s free email newsletter, please find it here. Or follow our posts on Threads, Facebook, BlueSky or Mastodon.
If you would like to support the mission of Open Culture, consider making a donation to our site. It’s hard to rely 100% on ads, and your contributions will help us continue providing the best free cultural and educational materials to learners everywhere. You can contribute through PayPal, Patreon, and Venmo (@openculture). Thanks!
Related Content:
The Epic of Gilgamesh, the Oldest-Known Work of Literature in World History
World Literature in 13 Parts: From Gilgamesh to García Márquez
20 New Lines from The Epic of Gilgamesh Discovered in Iraq, Adding New Details to the Story