Today it would be viewed as cultural appropriation writ large, but when Louis XIV ordered the construction of a 5‑building pleasure pavilion inspired by the Porcelain Tower of Nanjing (a 7th Wonder of the World few French citizens had viewed in person) as an escape from Versailles, and an exotic love nest in which to romp with the Marquise de Montespan, he ignited a craze that spread throughout the West.
Chinoiserie was an aristocratic European fantasy of luxurious Eastern design, what Dung Ngo, founder of AUGUST: A Journal of Travel + Design, describes as “a Western thing that has nothing to do with actual Asian culture:”
Chinoiserie is a little bit like chop suey. It was wholesale invented in the West, based on certain perceptions of Asian culture at the time. It’s very watered down.
And also way over the top, to judge by the rapturous descriptions of the interiors and gardens of Louis XIV’s Trianon de Porcelaine, which stood for less than 20 years.
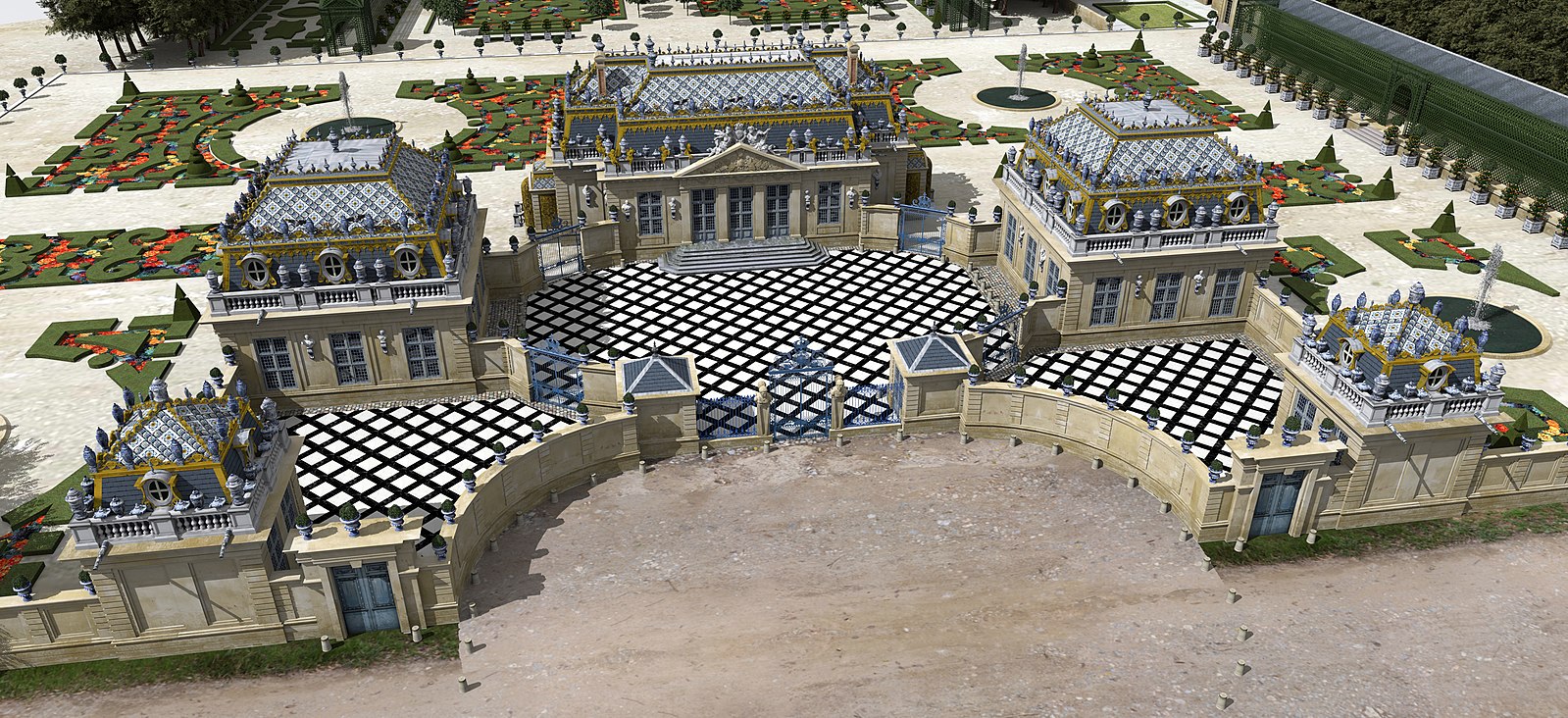

Image by Hervé Gregoire, via Wikimedia Commons
The blue-and-white Delft tiles meant to mimic Chinese porcelain swiftly fell into disrepair and Madame de Montespan’s successor, her children’s former governess, the Marquise de Maintenon, urged Louis to tear the place down because it was “too cold.”
Her lover did as requested, but elsewhere, the West’s imagination had been captured in a big way.
The burgeoning tea trade between China and the West provided access to Chinese porcelain, textiles, furnishings, and lacquerware, inspiring Western imitations that blur the boundaries between Chinoiserie and Rococo styles
This blend is in evidence in Frederick the Great’s Chinese House in the gardens of Sanssouci (below).
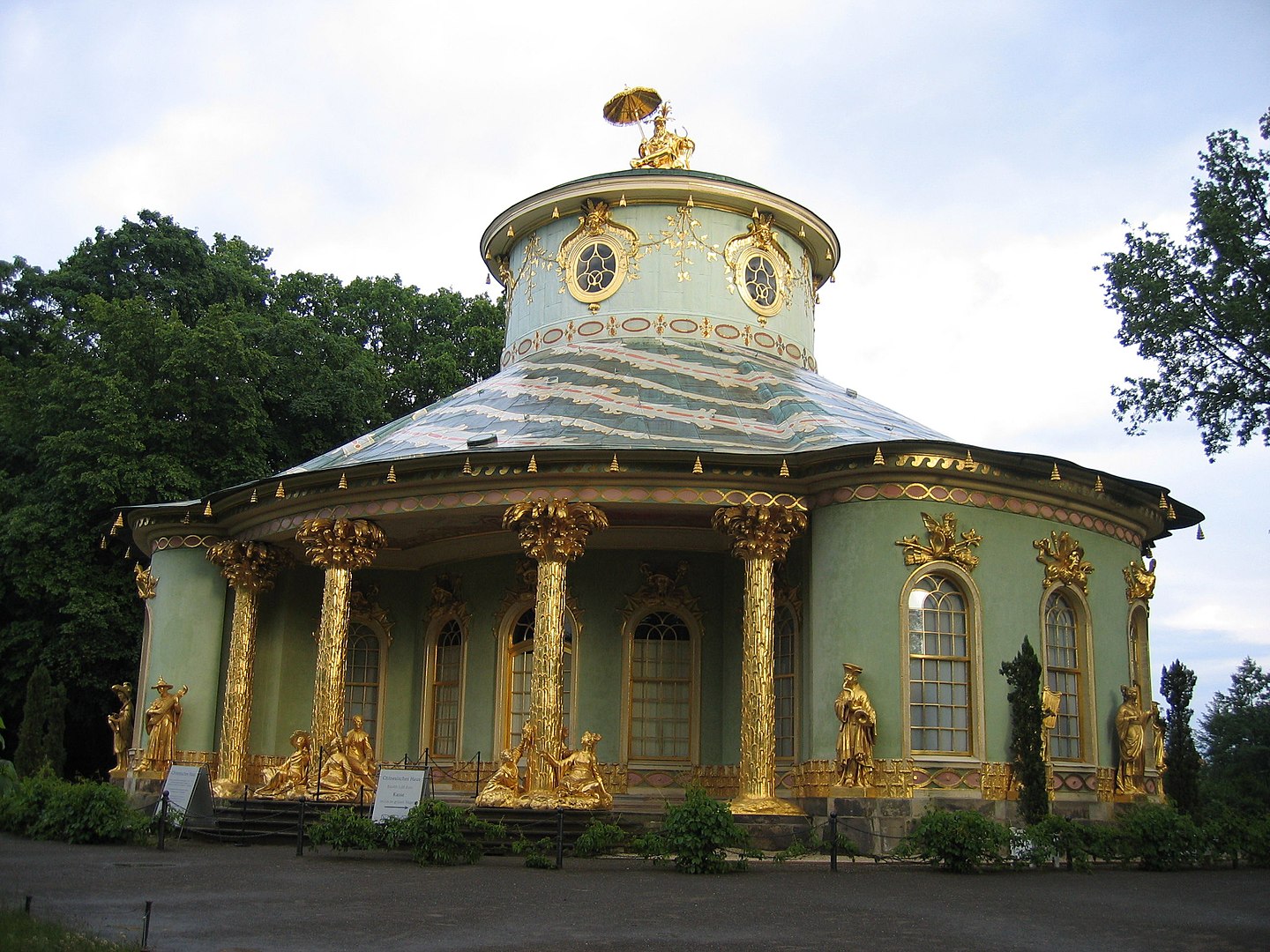

Image by Johann H. Addicks, via Wikimedia Commons
Dr Samuel Wittwer, Director of Palaces and Collections at the Prussian Palaces and Gardens Foundation, describes how the gilded figure atop the roof “is a mixture of the Greek God Hermes and the Chinese philosopher Confucius:”
His European face is more than just a symbol of intellectual union between Asia and Europe…The figure on the roof has an umbrella, an Asian symbol of social dignity, which he holds in an eastern direction. So the famous ex oriente lux, the good and wise Confucian light from the far east, is blocked by the umbrella. Further down, we notice that the foundations of the building seem to be made of feathers and the Chinese heads over the windows, resting on cushions like trophies, turn into a monkey band in the interior. The frescoes in the cupola mainly depict monkeys and parrots. As we know, these particular animals are great imitators without understanding.
Frederick’s enthusiasm for chinoiserie led him to engage architect Carl von Gontard to follow up the Chinese House with a pagoda-shaped structure he named the Dragon House (below) after the sixteen creatures adorning its roof.
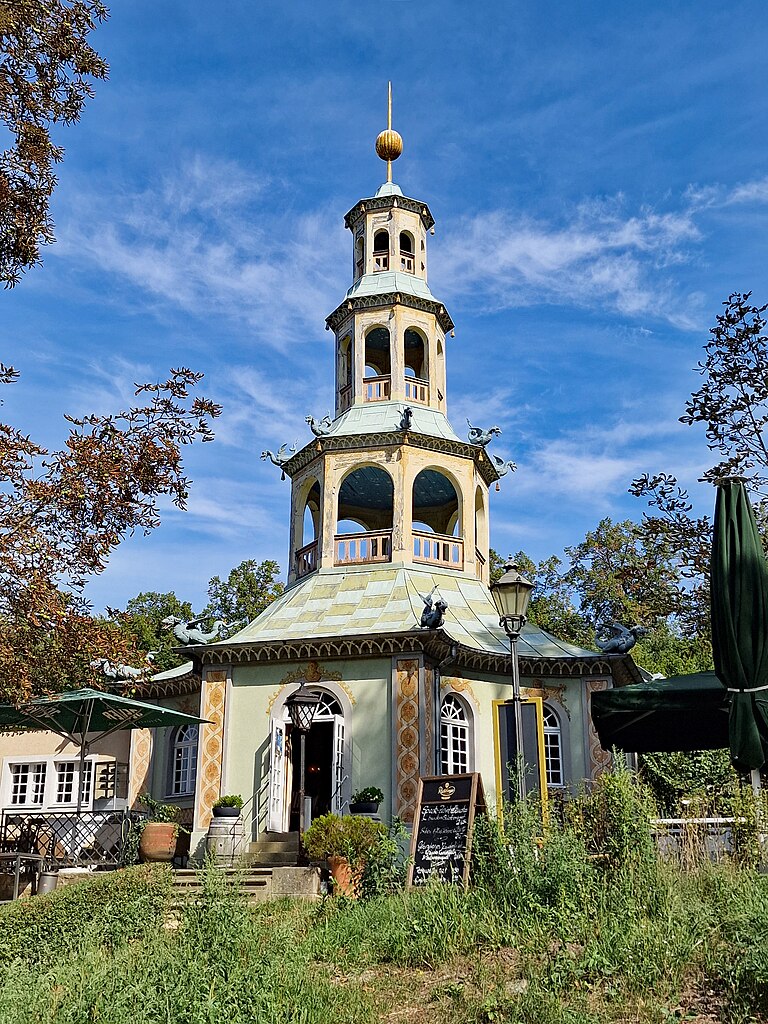

Image by Rigorius, via Wikimedia Commons
Dragons also decorate the roof of the Great Pagoda in London’s Kew Gardens, though the gilded wooden originals either succumbed to the elements or were sold off to settle George IV’s gambling debts in the late 18th century.
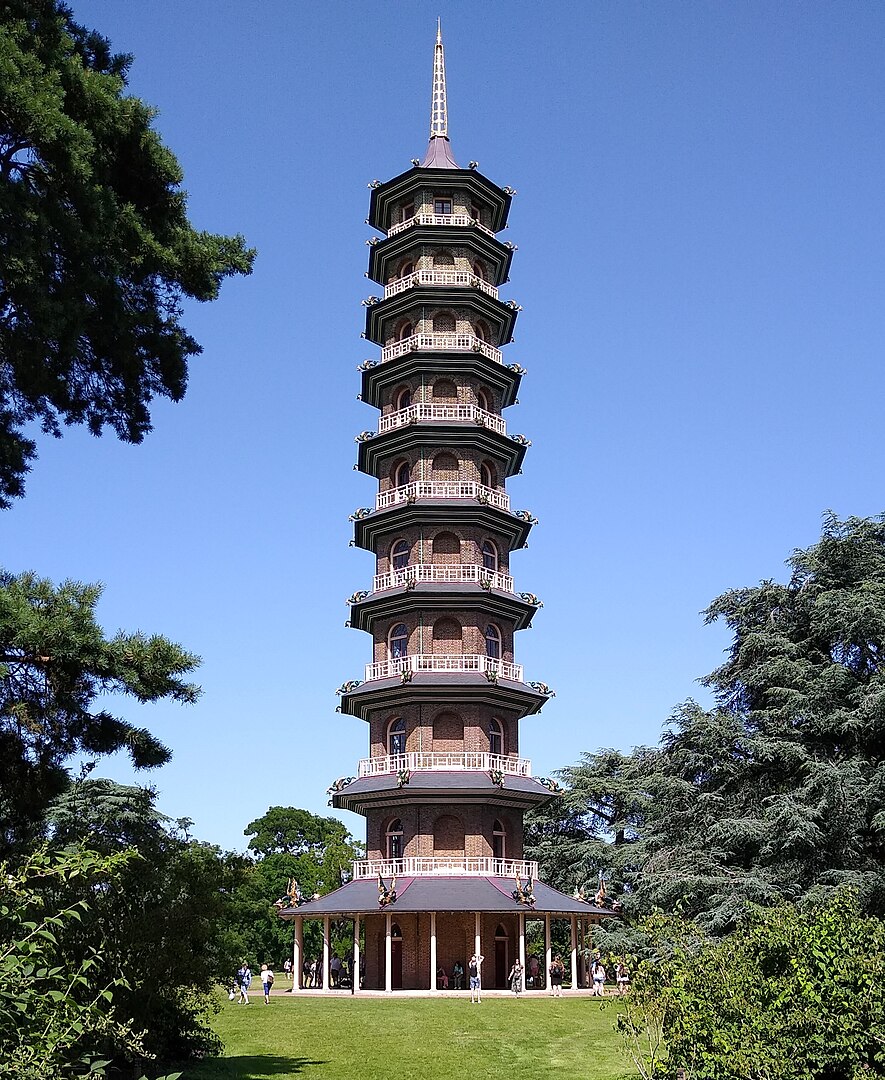

Image by MX Granger, via Wikimedia Commons
There are even more dragons to be found on the Chinese Pavilion at Drottningholm, Sweden, an architectural confection constructed by King Adolf Fredrik as a birthday surprise for his queen, Louisa. The queen was met by the entire court, cosplaying in Chinese (or more likely, Chinese-inspired) garments.
Not to be outdone, Russia’s Catherine the Great resolved to “capture by caprice” by building a Chinese Village outside of St. Petersburg.
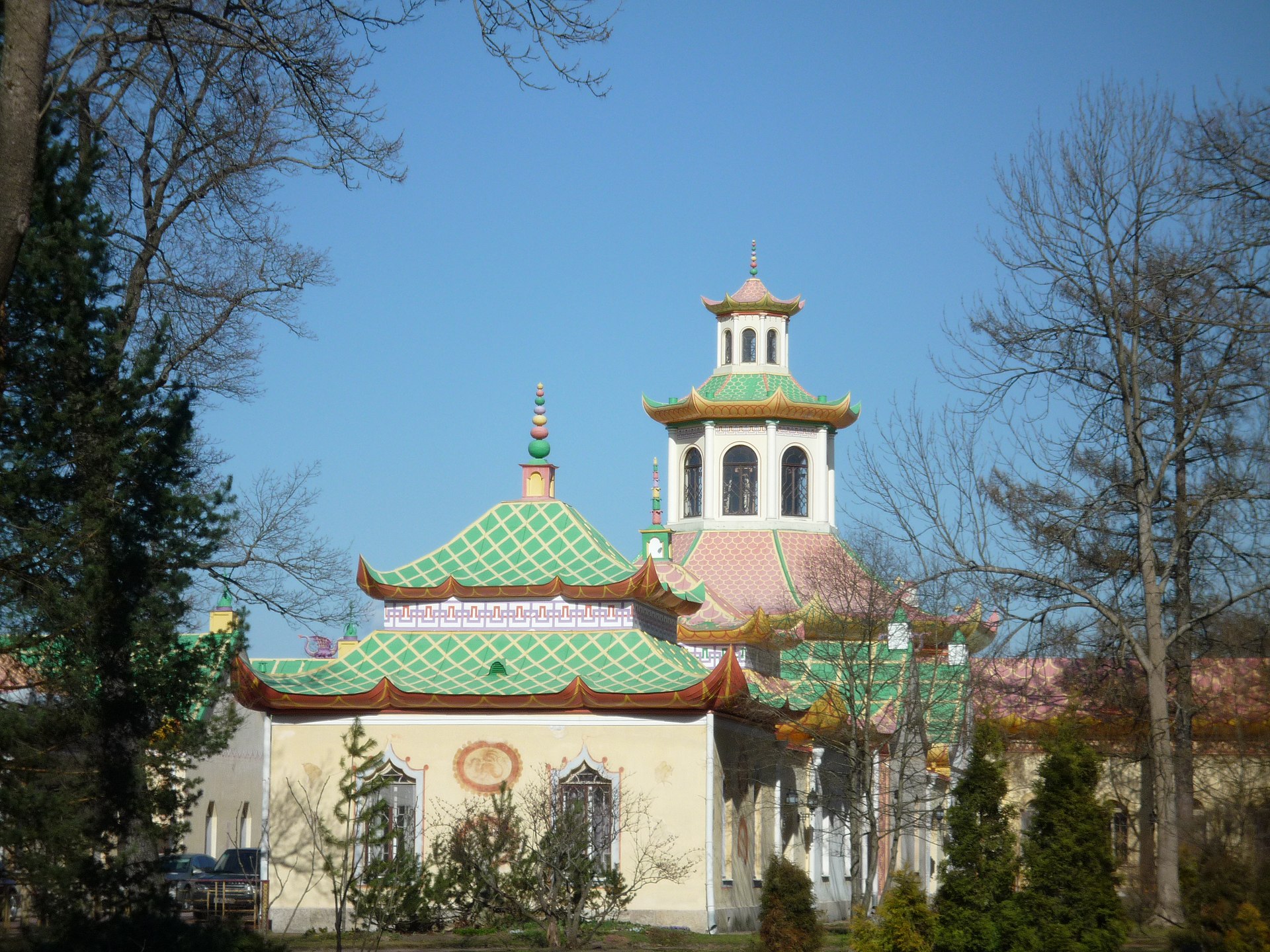

Image by Макс Вальтер, via Wikimedia Commons
Architect Charles Cameron drew up plans for a series of pavilions surrounding a never-realized octagonal-domed observatory. Instead, eight fewer pavilions than Cameron originally envisioned surround a pagoda based on one in Kew Gardens.
Having survived the Nazi occupation and the Soviet era, the Chinese Village is once again a fantasy plaything for the wealthy. A St. Petersburg real estate developer modernized one of the pavilions to serve as a two-bedroom “weekend cottage.”
Given that no record of the original interiors exists, designer Kirill Istomin wasn’t hamstrung by a mandate to stick close to history, but he and his client still went with “numerous chinoiserie touches” as per a feature in Elle Decor:
Panels of antique wallpapers were framed in gilded bamboo for the master bedroom, and vintage Chinese lanterns, purchased in Paris, hang in the dining and living rooms. The star pieces, however, are a set of 18th-century porcelain teapots, which came from the estate of the late New York socialite and philanthropist Brooke Astor.
Explore cultural critic Aileen Kwun and the Asian American Pacific Islander Design Alliance’s perspective on the still popular design trend of chinoiserie here.
h/t Allie C!
Related Content
How the Ornate Tapestries from the Age of Louis XIV Were Made (and Are Still Made Today)
– Ayun Halliday is the Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine and author, most recently, of Creative, Not Famous: The Small Potato Manifesto and Creative, Not Famous Activity Book. Follow her @AyunHalliday.