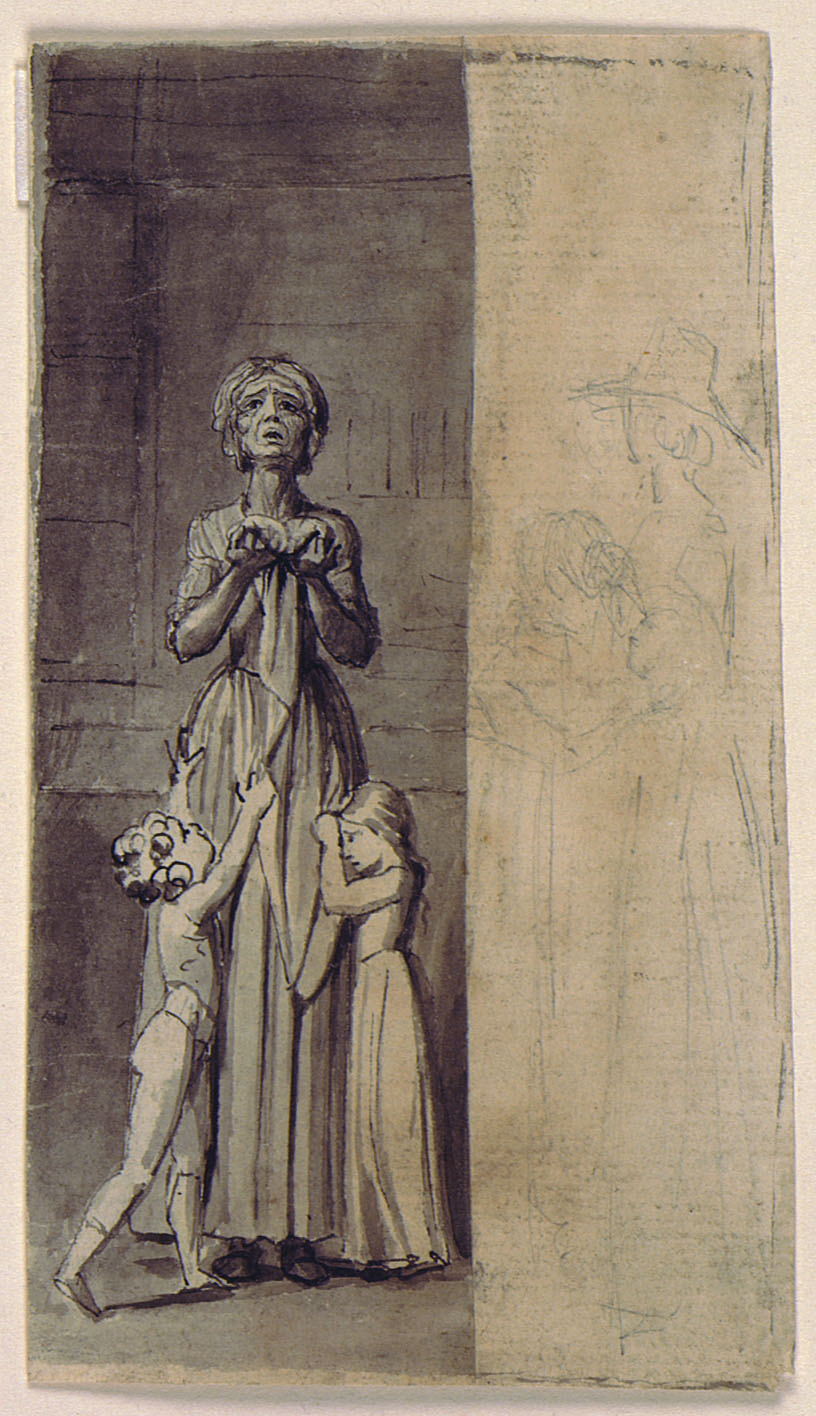
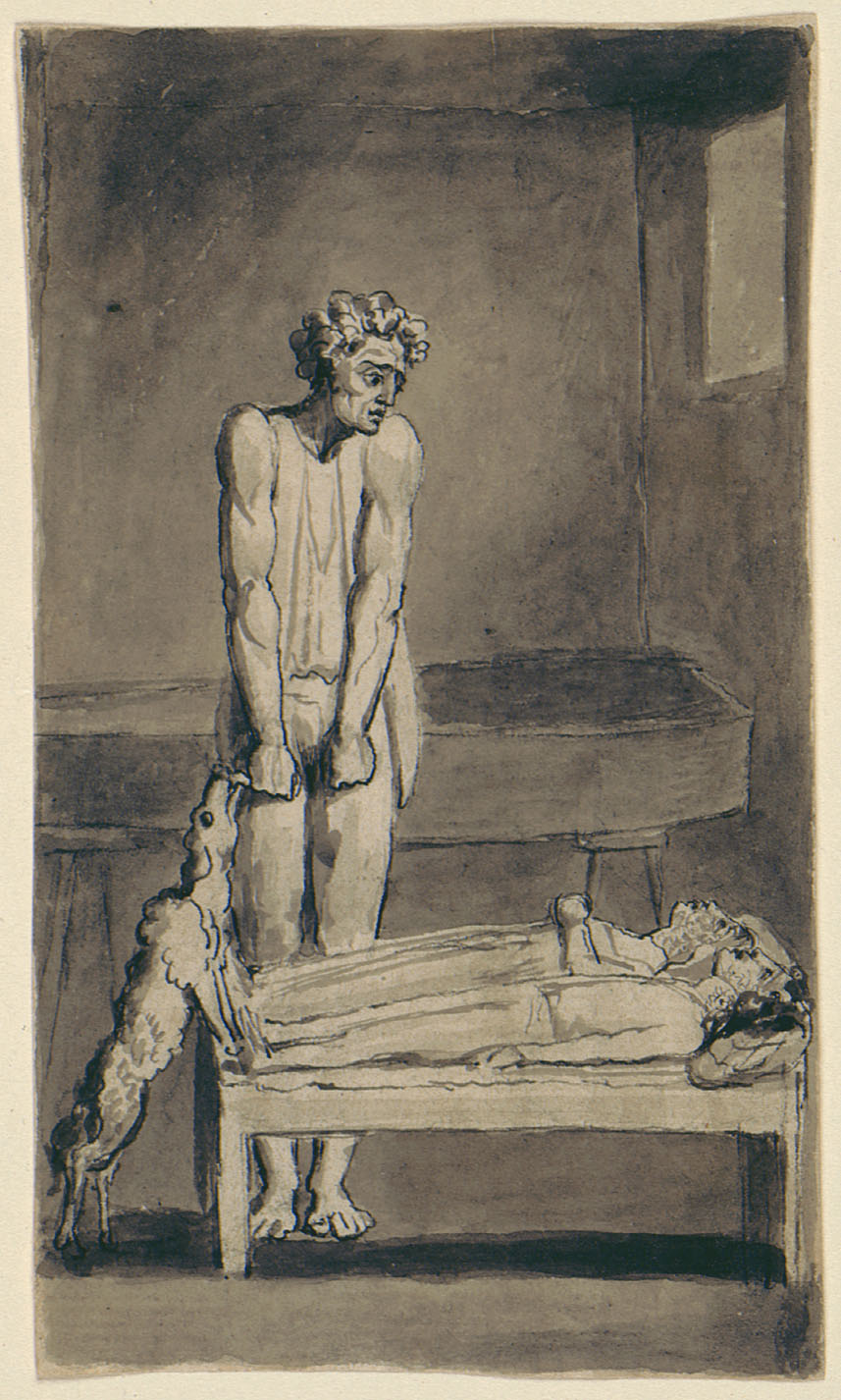
In August of 1918, a group of sumo wrestlers returned to Japan from an exhibition in Taiwan. When they came down with an illness it was first diagnosed as bronchitis or pneumonia. In fact, they had returned with the Spanish Flu.
The “Sumo Flu,” as it was first called by some in the Japanese press, was not taken as seriously as the more prevalent cholera, which had a higher death rate at the time. But cholera was not as infectious. By the time the Spanish Flu had burned its way through the population of Japan it would leave behind nearly half a million dead, either from the flu itself or secondary health complications.
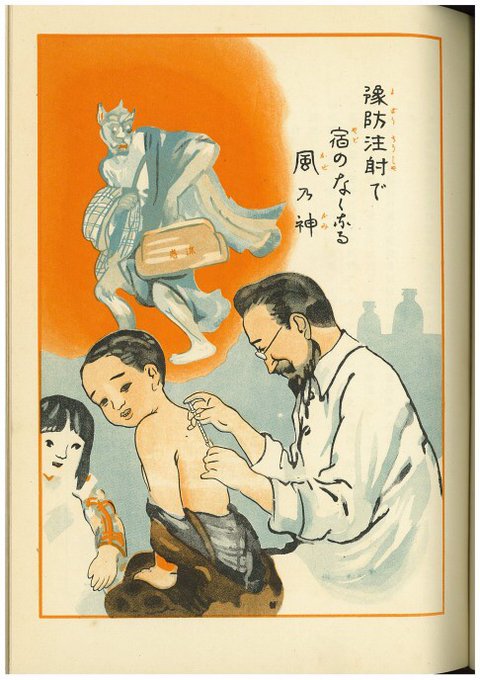
These posters (seen above and throughout this post) were part of Japan’s Central Sanitary Bureau’s plan to educate the public, part of a 455-manual that detailed symptoms and prescriptions, and suggested four rules to avoid contracting the virus and spreading it to others.

Right now, a lot of us are trying to do number one–Stay Away from Others–without going crazy, some of us are following number two (Cover Your Mouth and Nose), everybody’s waiting for number three (Get Vaccinated), and if you replace “Gargle” (Rule Number 4) with “anxiety drinking,” well we’ve got number four covered.
Back up to Number Three: the vaccine in question at that time helped with symptoms of pneumonia, which was a secondary cause of death. If a person’s immune system could fight off the lung infection part of the flu, they stood a better chance of survival.
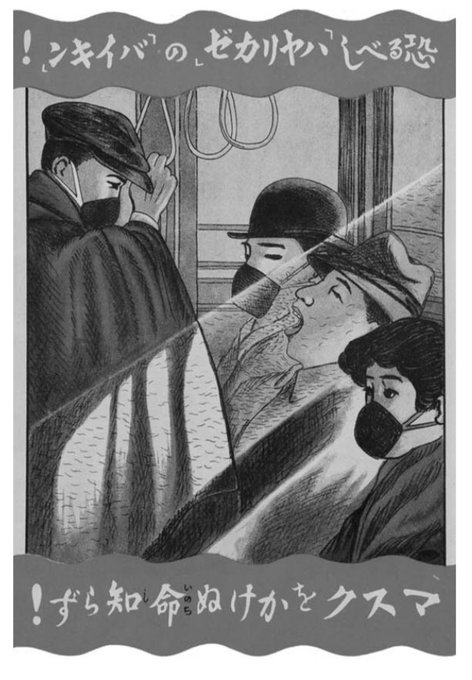
And for Number Two, the Japanese response of wearing face masks to fight infection has continued to this day. Anyone who has visited Japan, especially during cold and flu season, will have noticed the routine use of masks. Will other countries see this become a tradition in the future? We will have to wait and find out.
The central government of Japan, as well as most places around the globe in 1918, did not have the science or knowledge to treat the virus or enforce rules. A lot of decisions for the public were left to various prefectures to decide. Most doctors and researchers were already busy fighting cholera (as mentioned above) and tuberculosis. For a while, the virus was misidentified as a bacteria. And just like in America in 1919, the Japanese public thought things had gotten back to normal when the initial cases dropped–they were sadly mistaken and, after letting its guard down, the Japanese were hit with a second wave, with a mortality rate five times that of the first wave. As it spread from the city to the countryside, the Spanish Flu wiped out entire villages. Quackery and snake oil salesmen promised miracle cures. Others turned to spiritualism, prayer, and special devotional temple visits. The virus didn’t care.
But it also soon fizzled out. Japan reported no new cases in June of 1919, and that was that. (Currently, that does not seem to be the case in Wuhan or Germany.)
As the saying goes, history doesn’t repeat, but it often rhymes, and so take these posters as a warning and as a form of reassurance that we will get through this.
Related Content:
Pandemic Literature: A Meta-List of the Books You Should Read in Coronavirus Quarantine
The History of the Plague: Every Major Epidemic in an Animated Map
Ted Mills is a freelance writer on the arts who currently hosts the Notes from the Shed podcast and is the producer of KCRW’s Curious Coast. You can also follow him on Twitter at @tedmills, and/or watch his films here.