Deservedly or not, British care homes have acquired a reputation as especially dreary places, from Victorian novels to dystopian fiction to the flat affect of BBC documentaries. Martin Parr gave the world an especially moving example of the care home documentary in his 1972 photo series on Prestwich Asylum, outside Manchester. The compelling portraits humanize people who were neglected and ignored, yet their lives still look bleak in that austerely post-war British institution kind of way.
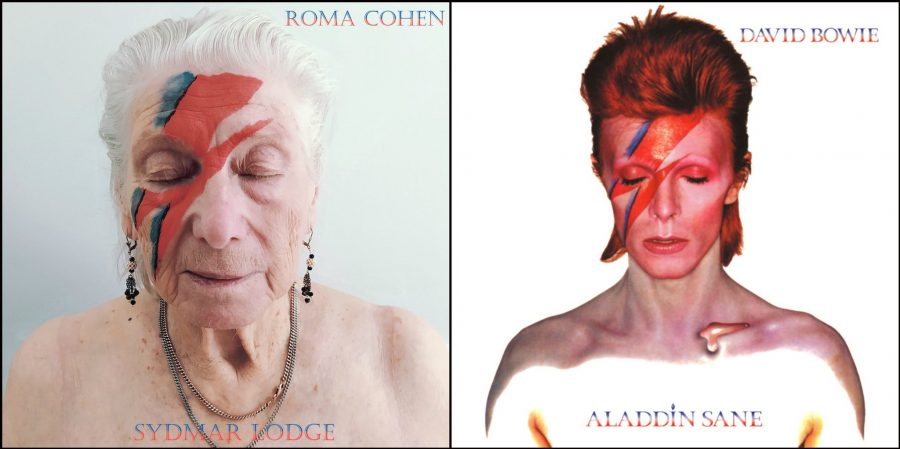
One cannot say anything of the kind of the photo series represented here, which casts residents of Sydmar Lodge Care Home in Edgeware, England as rock stars, digitally recreating some of the most famous album covers of all time. This is not, obviously, a candid look at residents’ day-to-day existence. But it suggests a pretty cheerful place. “The main aim was to show that care homes need not be a sad environment, even during this pandemic,” says the photos’ creator Robert Speker, the home’s activities manager.


“Speker tweeted side-by-side photos of the original covers and the Sydmar Lodge residents’ new takes, and the tweets quickly took off,” NPR’s Laurel Wamsley writes. He’s made it clear that the primary audience for the recreated covers is the residents themselves: Isolated in lockdown for the past four months; cut off from visits and outings; suffering from an indefinite suspension of familiar routines.
Speker does not deny the grim reality behind the inspiring images. “Elderly people will remain in lockdown for a long time,” he writes on a GoFundMe page he created to help support the home. “It could be months before the situation changes for them.”
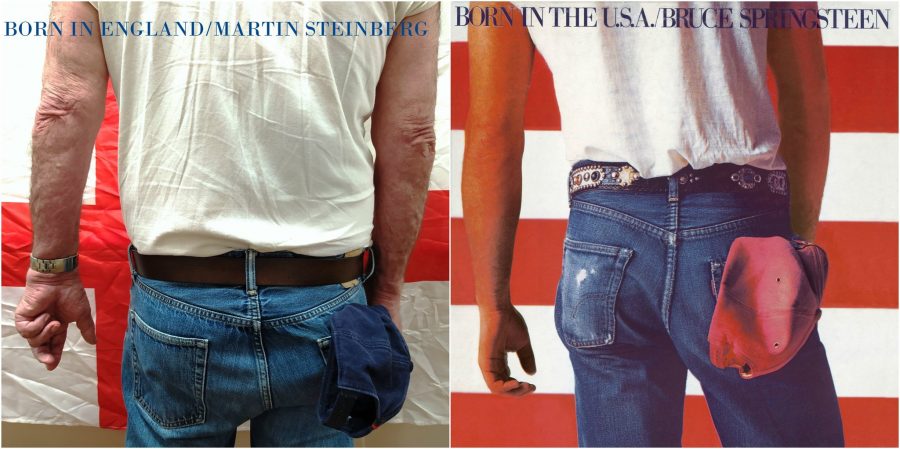

But he is optimistic about his abilities to “make their time as happy and full of enjoyment and interest as possible.” Would that all nursing homes had such a dedicated, award-winning coordinator. Residents themselves, he wrote on Twitter, were “enthused and perhaps a bit bemused by the idea, but happy to participate.” When they saw the results—stunning Roma Cohen as Aladdin Sane, defiant Sheila Solomons as Elvis and The Clash’s Paul Simenon, casual Martin Steinberg as a “Born in England” Springsteen—they were delighted. Four of the home’s carers got their own cover, too, posed as Queen.
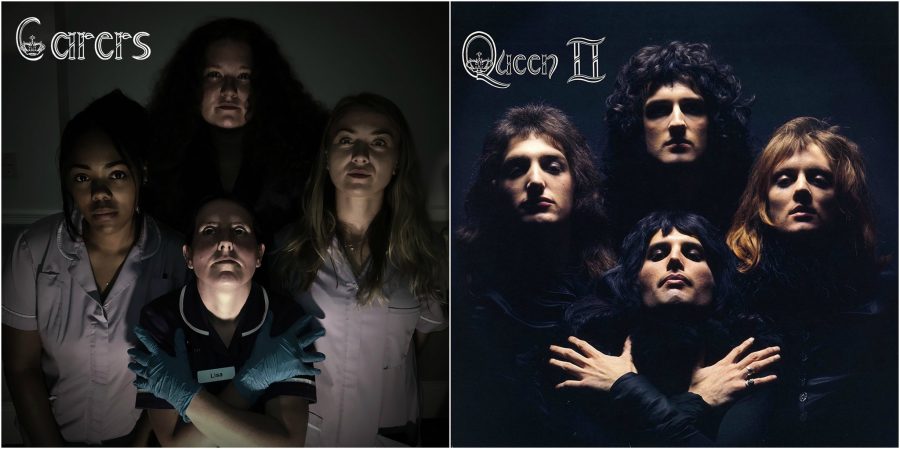

Residents, Speker said, were really “having a good giggle about it.” And we can too, as we bear in mind the many elderly people around us who have been locked in for months, with maybe many more months of isolation ahead. Not everyone is as talented as Robert Speker, who did the models’ makeup and tattoos himself (with hair by a care home manager), as well as taking all the photographs and editing the images to convincingly mimic the poses, composition, lighting, font, and color schemes of the originals. But let’s hope his work is a spark that lights up nursing homes and care facilities with all sorts of creative ideas to keep spirits up. See several more covers below and the rest on Twitter.
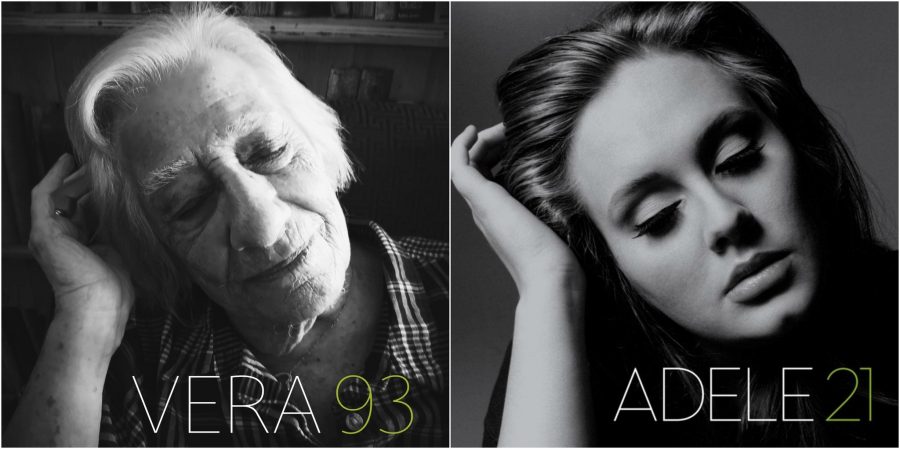
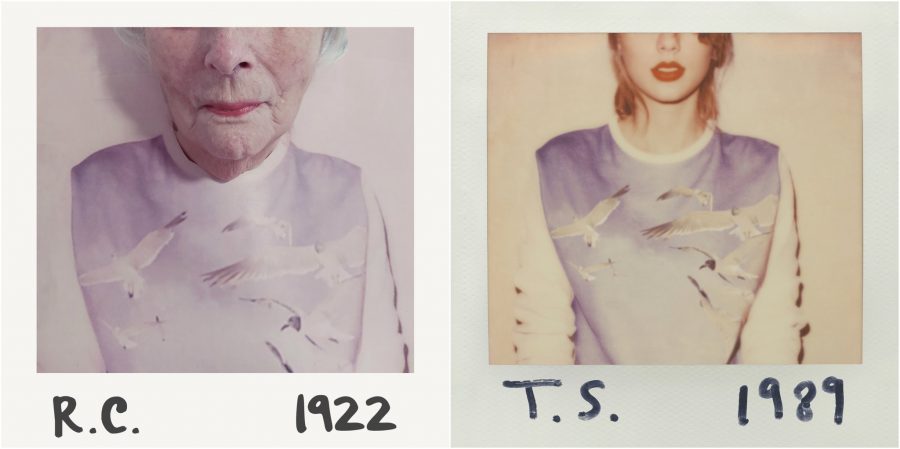




Related Content:
People Pose in Uncanny Alignment with Iconic Album Covers: Discover The Sleeveface Project
The History of the Fisheye Photo Album Cover
Dyson Creates 44 Free Engineering & Science Challenges for Kids Quarantined During COVID-19
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness