Each generation takes what it needs from early punk and discards what it doesn’t, so that countless subgenres have descended from a small, eccentric collection of punk bands from the late 1970s. The speed and brute simplicity of the Ramones took over in the 80s. The Clash’s strident, reggae-inflected anthems guided much of the 90s. The angular art rock and new wave disco of Television, Talking Heads, and Blondie defined the 2000s.
But some things became almost terminally passé, or terminally stupid, after punk’s first wave: like signing to major labels or wearing swastikas, ironically or otherwise. Already out of fashion by 1978, the first punk dance, the pogo, was so tragically unhip that Debbie Harry pronounced it dead on arrival in the U.S. on famed Manhattan cable access show TV Party, above. She offers to demonstrate it anyway as a “historical” artifact.
Her commentary seems like both a sarcastic rip on the ridiculous spread of trends and a genuine warning to those who might try to make this, like, a thing in New York. Don’t bring a creaky pogo stick with you to the club. Do pour beer over your head after a sweaty half-hour of whatever dance you do. There was so much to learn about punk etiquette even then. Unless you happened to be Sid Vicious, or in the audience of the first Sex Pistols shows. Then it was all fair game.
The pogo originated, so the lore goes, with Sid. As Steve Severin of Siouxsie and the Banshees remembers it, “We first met [Sid] at one of the concerts. He began bouncing around the dance floor, the so called legend of the pogo dance. It was merely Sid jumping up and down, trying to see the band, leaping up and down because he was stuck in the back somewhere.” Just as everyone who saw the Sex Pistols started their own band, everyone who saw Sid bounce around started to pogo.
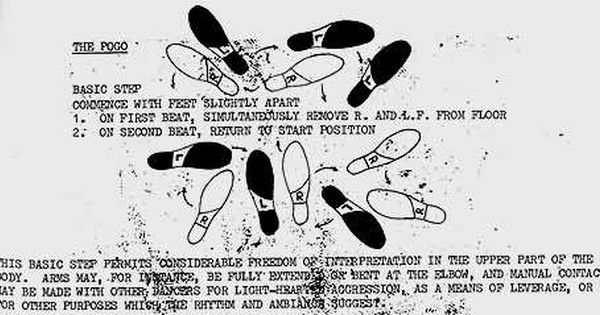
What at first looks like harmless fun, especially compared to the brutal mosh pits that took over for the pogo, was anything but. “Pogoing was very violent and very painful,” one eyewitness remembers. “People were not quite crushed to death, but serious injuries occurred.” We might rethink Men Without Hats’ “The Safety Dance,” the 80s hit written in defense of pogoing. Lead singer Ivan Doroschuk penned the tune after he was kicked out of a club for doing the pogo. “I think people can relate to the empowering kind of message of ‘The Safety Dance,’” he says.
“The Safety Dance” would not have been the empowering worldwide smash it was had it been called “Pogo Dancing,” a minor hit for the Vibrators in 1976. Not nearly as iconic, and overshadowed by a hipper dance of the same name in the 80s, was the robot, elegized by The Saints in “Doing the Robot.” This dance was “both more expressive and less spontaneous,” as cultural theorist Dick Hebdige describes it in Subculture: The Meaning of Style, consisting of “barely perceptible twitches of the head or hands or more extravagant lurches (Frankenstein’s first steps?) which were abruptly halted at random points.” Hardly as practical as the pogo, but probably a lot safer.
via Boing Boing
Related Content:
How Blondie’s Debbie Harry Learned to Deal With Superficial, Demeaning Interviewers
The 100 Top Punk Songs of All Time, Curated by Readers of the UK’s Sounds Magazine in 1981
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness