We surround the phrase “ahead of its time” with a mystical aura. But just because an idea shows up earlier than we expect does not mean it was ever a good idea for human progress. Take, for example, the idea to rain incendiary devices on the heads of civilian populations in wartime. Recent iterations of this technology — unmanned drones surgically bombing weddings and funerals — may be an improvement over Hiroshima or napalm-happy helicopter pilots like Apocalypse Now’s Bill Kilgore. But drones have not, thereby, rendered the nuclear option or trigger-happy death from above obsolete, or made mass civilian casualties less tragic and unnecessary, comparisons of raw numbers aside.
Drone bombing is one of those ideas that showed up ahead of its time — at the very first use of aerial bombing of any kind. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) were launched in the service of a military operation 30 years before Edison harnessed electricity for home use.
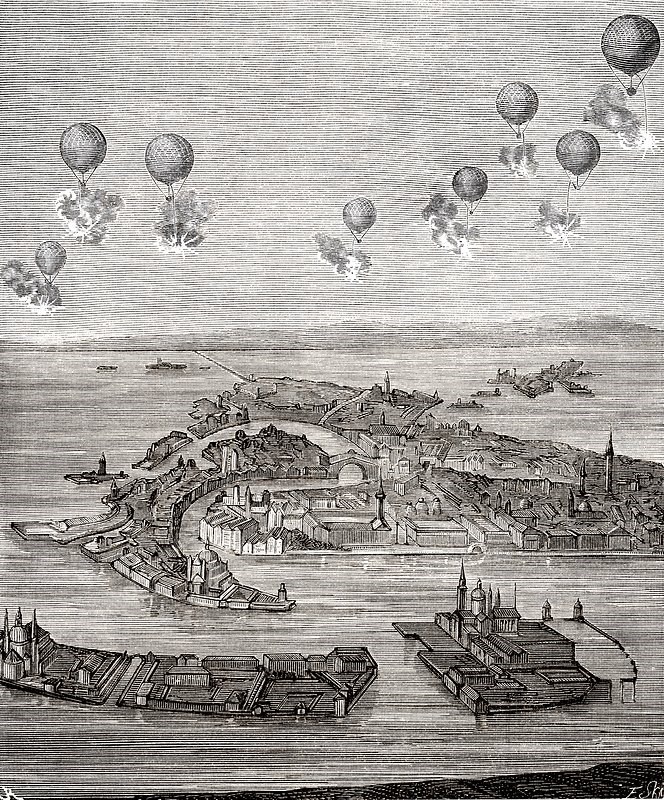
In 1849, remote piloting was hardly possible. But it was possible to launch a fleet of hot air balloons loaded with explosives from a ship and send them in the general direction of a target. That’s what the Austrian army did — twice — over Venice, in a campaign to recapture the city when its citizens rebelled against imperial rule and built their own republic. Luckily for Venice, the first use of naval air power was also the least effective.

The balloons “carried 33 pounds of explosives,” writes Monash University professor Russell Naughton, “set with a half-hour time fuse, and troops scurried around with them to launch them into the proper wind currents.” The idea for the bombardment came from an Austrian artillery lieutenant named Franz von Uchatius and was initially carried out on July 12, 1849. This attempt “failed because the wind was not in Austria’s favor,” writes Weapons and Warfare, quoting from a contemporary account in Time magazine:
The balloons appeared to rise to about 4,500 ft. Then they exploded in midair or fell into the water, or, blown by a sudden southeast wind, sped over the city and dropped on the besiegers. Venetians, abandoning their homes, crowded into the streets and squares to enjoy the strange spectacle. … When a cloud of smoke appeared in the air to make an explosion, all clapped and shouted. Applause was greatest when the balloons blew over the Austrian forces and exploded, and in such cases the Venetians added cries of ‘Bravo!’ and ‘Good appetite!’
More spectacle than threat, the balloon bombs might have been abandoned as a failed experiment, but the Austrians were persistent; they had besieged the city, determined to subdue it. Another attack on August 22 seems to have also done more damage to the Austrians than their targets. Although the balloons could not be piloted, the detonation of their charges was controlled, Scientific American wrote that year, “by electro magnetism by means of a long isolated copper wire with a large galvanic battery placed on the shore. The bomb falls perpendicularly, and explodes on reaching the ground” … theoretically.
It is not clear from the sources how many bombs were launched. Numbers range from 2 to 200. In any case, the bombing would have little effect on ending the siege, which went on for five more months afterward, and they received little notice in the press. They did, however, have the effect after their second appearance of producing “extreme terror,” the British Morning Chronicle reported, documenting the first appearance of “shock and awe.” And terror was “clearly what was intended,” Brett Holman writes at Airminded, rather than a strategic offensive. “The bombs used were filled with shrapnel, which isn’t much use for anything but killing and maiming people. So there were few qualms on the part of the Austrians about targeting and killing civilians.” They were simply killed more efficiently with conventional artillery and starvation.
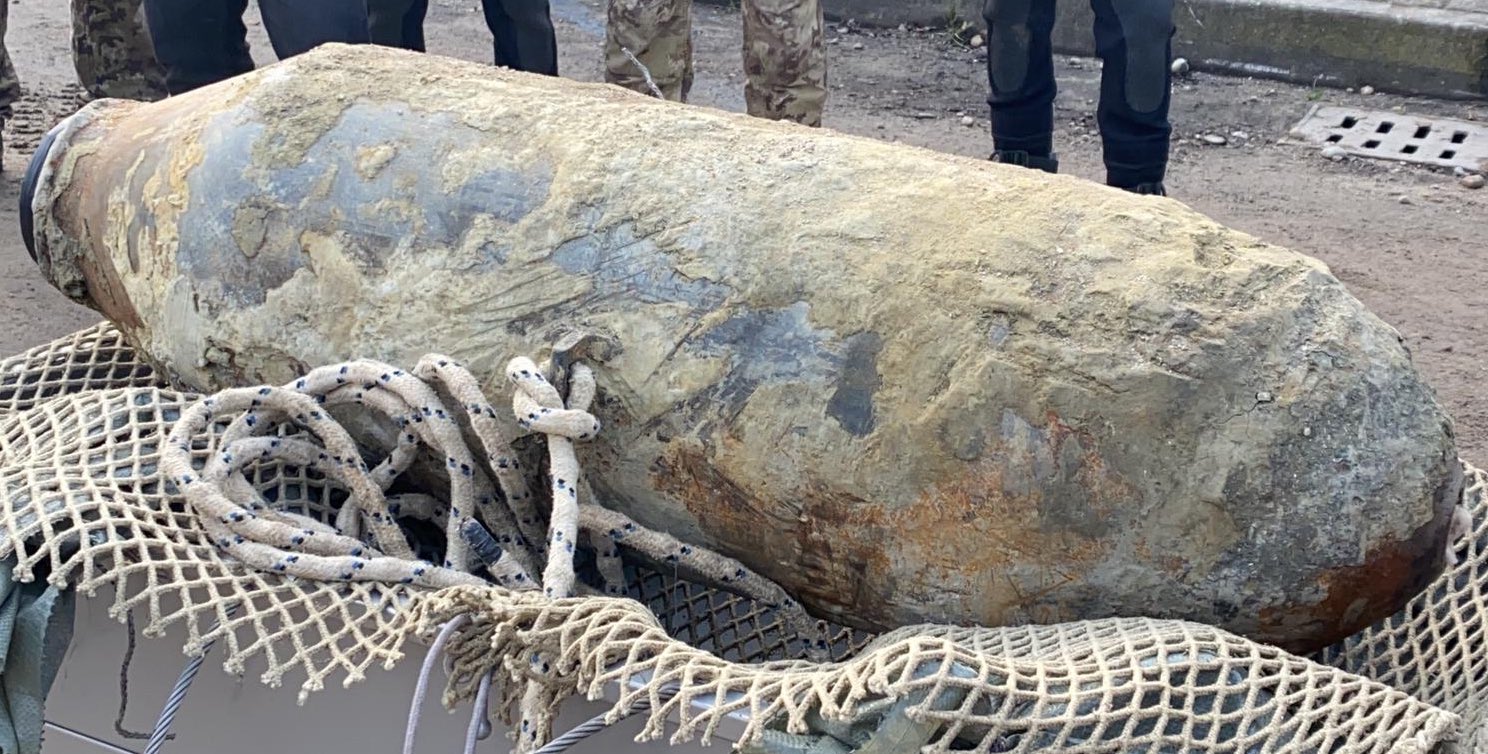

The example of the Austrians was not followed by other armies, who weren’t eager to have explosive balloons blow back on their own lines. The idea of bombing cities from the air, writes Holman, “had to be invented all over again. Which it was, of course, and Venice’s next air raid was on 24 May 1915.”
Just last year, the entire city shut down — “even planes were barred from flying to and from Venice’s Marco Polo Airport,” DW reported — as authorities led an effort to “remove and defuse a World War II-era bomb” on what local media dubbed “Bomba Day.”
via Marina Amaral
Related Content:
Watch Venice’s New $7 Billion Flood Defense System in Action
How Venice Works: 124 Islands, 183 Canals & 438 Bridges
A Drone’s Eye View of the Ruins of Pompeii
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness