No cartoon Dutch landscape omits a windmill. With their wooden frames and large blades, those mechanical structures have been used in the Netherlands since at least the twelfth century, first to pump water out of potentially arable lowlands, and later for such uses as sawing wood and pounding grain. Today, of course, there exist much more efficient technologies for those jobs, but the windmill nevertheless remains a Dutch cultural icon. In the Netherlands the wind itself also blows as strong as ever, just waiting to be harnessed: if not by industry, then perhaps by art. Enter Theo Jansen, inventor of the strandbeest — Dutch for “beach beast,” an apt description of its nature.
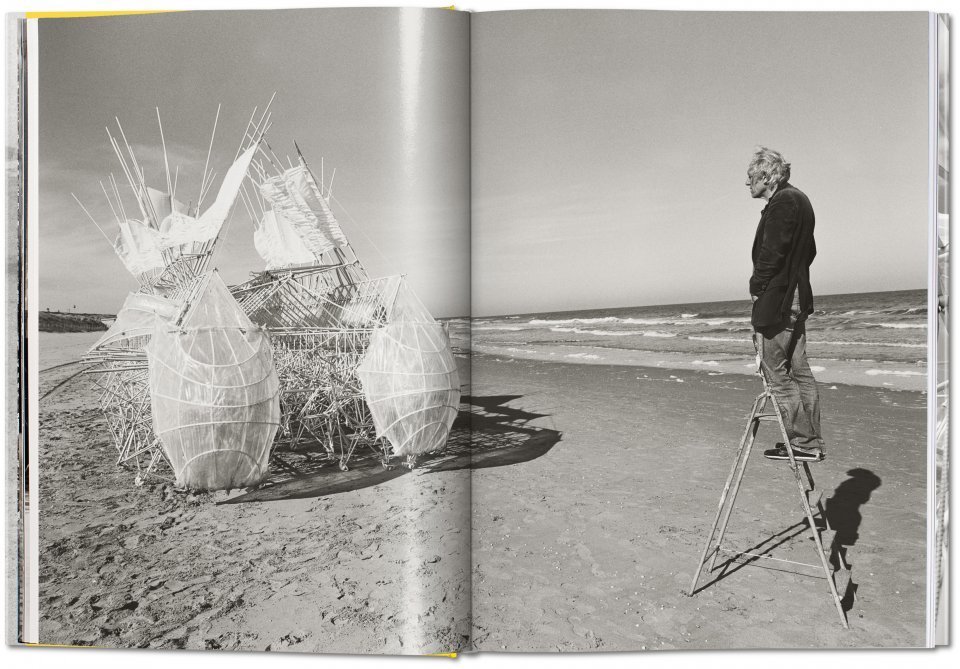

Elaborately constructed with off-the-shelf materials like wood, PVC piping, and sheets of fabric, Jansen’s large and fantastical-looking strandbeesten walk through the sand as if moving under their own volition. In fact they’re wind-powered kinetic sculptures, articulated in such a way as to make their movements look wholly organic.
Created for more than thirty years now through Jansen’s intelligent design, the strandbeesten are also subject to a process not unlike biological evolution. You can see it in the artist’s clip compilation at the top of the post and Taschen’s new book Strandbeest: The Dream Machines of Theo Jansen by photographer Lena Herzog (wife, incidentally, of Werner Herzog, a known appreciator of such “conquests of the useless”). You can also purchase mini models of the Strandbeest online.
“I make skeletons that are able to walk on the wind,” Jansen once said. “Over time, these skeletons have become increasingly better at surviving the elements such as storms and water and eventually I want to put these animals out in herds on the beaches, so they will live their own lives.” His goals also include equipping future generations of strandbeesten with a kind of mechanical artificial intelligence, which would let them avoid the kind of dangers that got their ancestors toppled or stuck. But in their sheer uncanny magnificence, even the least intelligent examples have fascinated the world. A few years ago Jansen and one of his creations even appeared on The Simpsons, suggesting that one day, cartoon Dutch landscapes may be incomplete without a strandbeest.
Related content:
Existential Moments with Theo Jansen and His Amazing Kinetic Sculptures, the Strandbeests
Behold the Kinetic, 39-Ton Statue of Franz Kafka’s Head, Erected in Prague
Metropolis II: Discover the Amazing, Fritz Lang-Inspired Kinetic Sculpture by Chris Burden
A Perfect Springtime Animation: The Windmill Farmer by Joaquin Baldwin
Alexander Calder’s Archive Goes Online: Explore 1400 Works of Art by the Modernist Sculptor
Pendulum Waves as Kinetic Art
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the Substack newsletter Books on Cities, the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.