What does it take to wear an ancient Roman toga with dignity and grace?
Judging from the above demonstration by Dr Mary Harlow, Associate Professor of Ancient History at the University of Leicester, a couple of helpers, who, in the first century CE, would have invariably been enslaved, and thus ineligible for togas of their own.
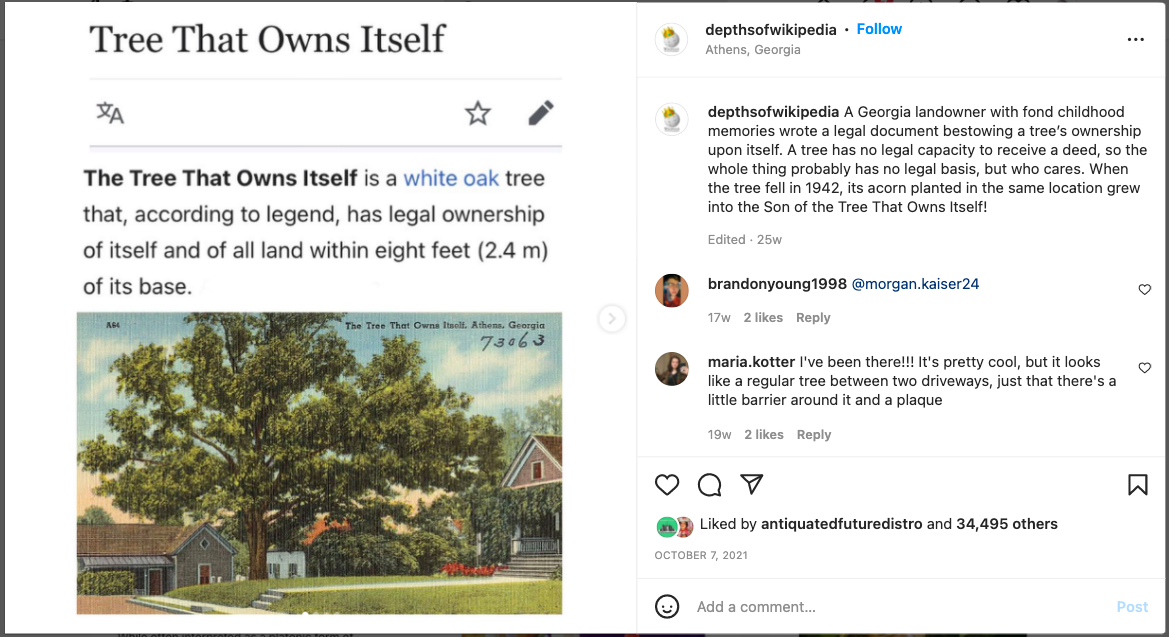
The iconic outer garments, traditionally made of wool, begin as single, 12–16m lengths of fabric.
Extra hands were needed to keep the cloth from dragging on the dirty floor while the wearer was being wrapped, to secure the garment with additional pleats and tucks, and to create the pouch-like umbo at chest level, in a manner as aesthetically pleasing as every other fold and drape was expected to be.
As formal citizen’s garb, the toga was suitable for virtually every public occasion, as well as an audience with the emperor.
In addition to slaves, the toga was off-limits to foreigners, freedmen, and, with the notable exception of adulteresses and prostitutes, women.
Wealthier individuals flaunted their status by accenting their outfit with stripes of Tyrian Purple.
The BBC reports that dying even a single small swatch of fabric this shade “took tens of thousands of desiccated hypobranchial glands wrenched from the calcified coils of spiny murex sea snails” and that thus dyed, the fibers “retained the stench of the invertebrate’s marine excretions.”
Achieving that Tyrian Purple hue was “a very smelly process,” Dr. Harlow confirms, “but if you could retain a little bit of that fishy smell in your final garment, it would show your colleagues that you could afford the best.”
Given the laundry-related revelations of some toga investigating students in Salisbury University’s Department of Theatre and Dance study abroad program, above, a fishy odor might not have been the greatest olfactory challenge associated with this garment.
The students also share how toga-clad Romans dealt with stairs, and introduce viewers to 5 forms of toga:
Toga Virilis — the toga of manhood
Toga Praetexta — the pre-toga of manhood toga
Toga Pulla — a dark mourning toga
Toga Candida- a chalk whitened toga sported by those running for office
Toga Picta- to be worn by generals, praetors celebrating games and consuls. The emperor’s toga picta was dyed purple. Uh-oh.

Their youthful enthusiasm for antiquity is rousing, though Quintilian, the first century CE educator and expert in rhetoric might have had some thoughts on their clownish antics.
He certainly had a lot of thoughts about togas, which he shared in his instructive masterwork, Institutio Oratoria:
The toga itself should, in my opinion, be round, and cut to fit, otherwise there are a number of ways in which it may be unshapely. Its front edge should by preference reach to the middle of the shin, while the back should be higher in proportion as the girdle is higher
behind than in front. The fold is most becoming, if it fall to a point a little above the lower edge of the tunic, and should certainly never fall below it. The other fold which passes obliquely like a belt under the right shoulder and over the left, should neither be too tight nor too loose. The portion of the toga which is last to be arranged should fall rather low, since it will sit better thus and be kept in its place. A portion of the tunic also should be drawn back in order that it may not fall over the arm when we are pleading, and the fold should be thrown over the shoulder, while it will not be unbecoming if the edge be turned back. On the other hand, we should not cover the shoulder and the whole of the throat, otherwise our dress will be unduly narrowed and will lose the impressive effect produced by breadth at the chest. The left arm should only be raised so far as to form a right angle at the elbow, while the edge of the toga should fall in equal lengths on either side.
Quintillian was willing to let some of his high standards slide if the wearer’s toga had been untidied by the heat of rousing oration:
When, however, our speech draws near its close, more especially if fortune shows herself kind, practically everything is becoming; we may stream with sweat, show signs of fatigue, and let our dress fall in careless disorder and the toga slip loose from us on every side…On the other hand, if the toga falls down at the beginning of our speech, or when we have only proceeded but a little way, the failure to replace it is a sign of indifference, or sloth, or sheer ignorance of the way in which clothes should be worn.
We’re pretty sure he would have frowned on classical archaeologist Shelby Brown’s experiments using a twin-size poly-blend bed sheet in advance of an early 21st-century College Night at the Getty Villa.
Prospective guests were encouraged to attend in their “best togas.”
Could it be that the party planners , envisioning a civilized night of photo booths, classical art viewing, and light refreshments in the Herculaneum-inspired Getty Villa, were so ignorant of 1978’s notorious John Belushi vehicle Animal House?
…Estne volumen in toga, an solum tibi libet me videre?
Related Content
- Ayun Halliday is the Chief Primatologist of the East Village Inky zine and author, most recently, of Creative, Not Famous: The Small Potato Manifesto. Follow her @AyunHalliday.