We may not know for sure the identity of Banksy, the English street artist famous for his social-commentary graffiti murals inspired and integrated with their surroundings. But given his apparent interests, we might have suspected him to turn up in Ukraine sooner or later. Recently posted by Banksy himself, the video above shows him at work in the region of Kyiv, the Ukrainian capital, each of which makes a visual comment on this year’s Russian invasion and the fortitude Ukraine’s people have shown against it. “As is typical of Banksy’s work,” writes The Art Newspaper’s Torey Akers, “the artist’s edits combine a satirist’s edge for winking commentary with a sincere investment in political solidarity.”
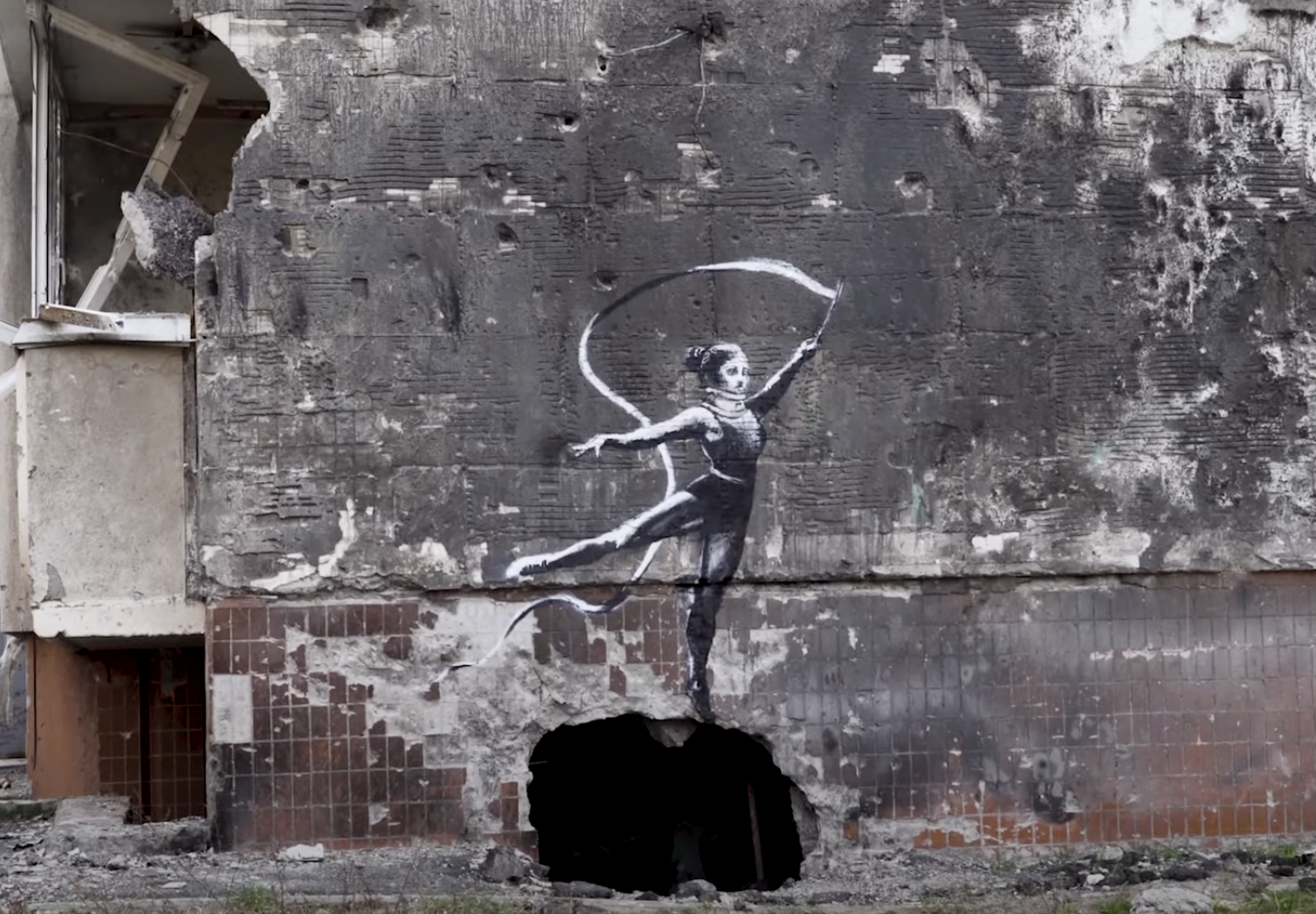
Smithsonian.com’s Jacquelyne Germain describes a few of Banksy’s new works in Ukraine, beginning with two in the nearly abandoned town of Borodyanka. “Painted on the side of a crumbling building,” one piece “depicts a gymnast doing a handstand on a pile of rubble.”
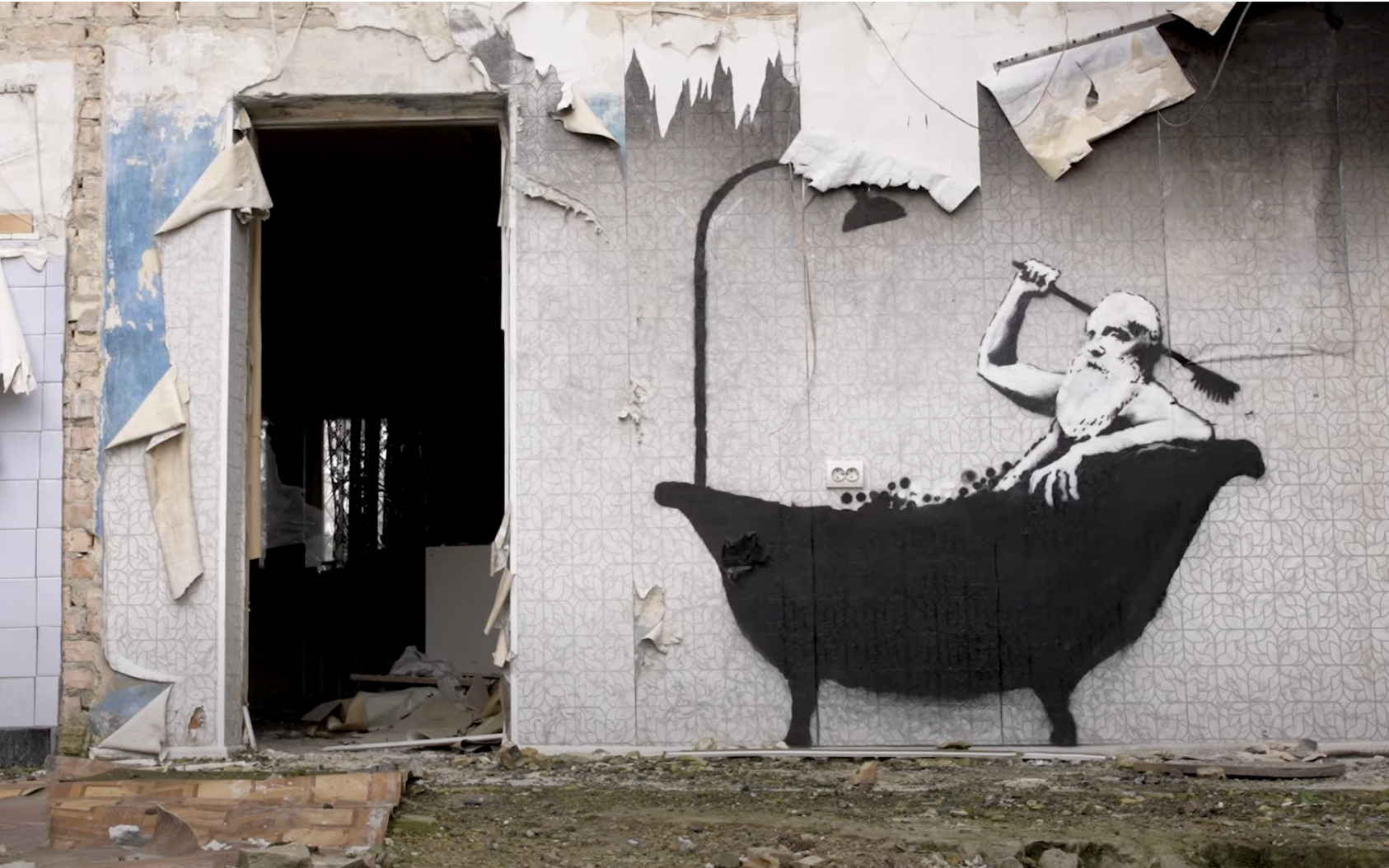

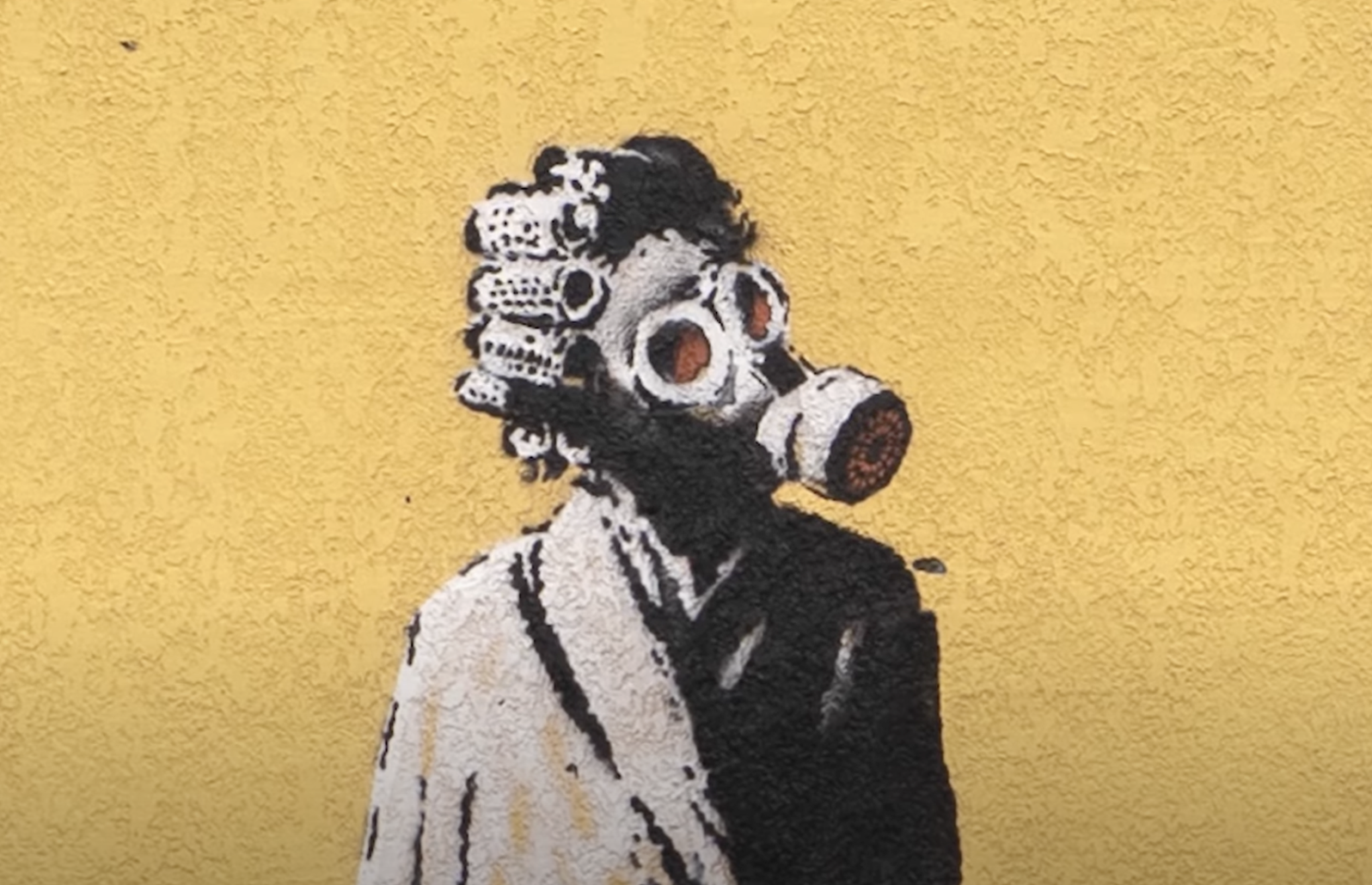
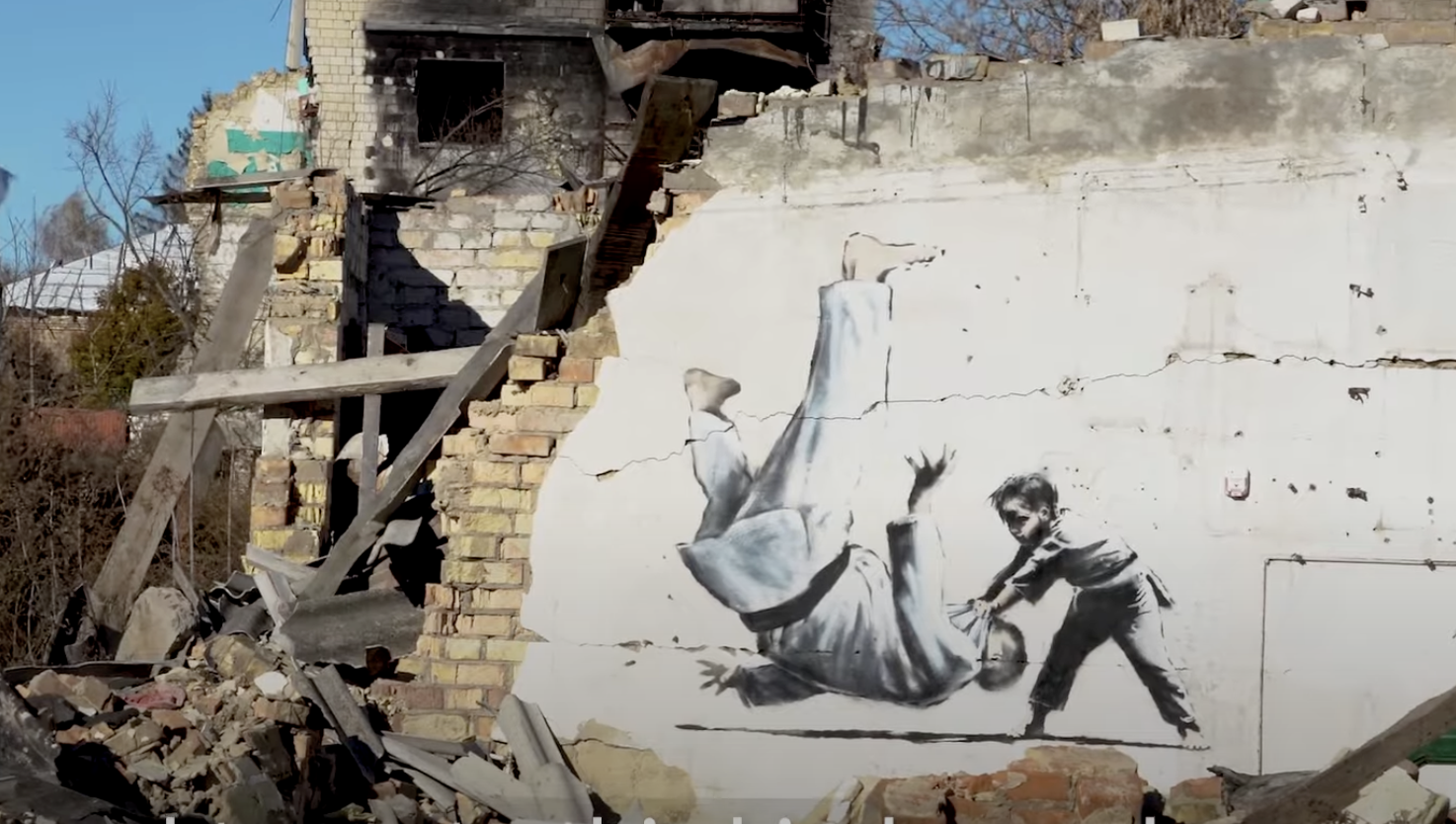
In another, “a young boy flips an older man onto his back in a judo match. Some speculate that the older man is Russian President Vladimir Putin, who is known to be a judo enthusiast.” (Banksy has developed a distinctive sensibility in his decades of public art, but subtlety isn’t its foremost element.) His images put up elsewhere “juxtapose wartime imagery with snapshots of civilian life: in one, children ride a metal tank trap as a seesaw,” and in another “a woman in her dressing gown wears a gas mask.”

The conflict in Ukraine now approaches its tenth month, with no clear signs of an end to the violence. Civilian life can’t go on, yet must go on, and it comes as no surprise that Banksy would find something to draw upon in that harrowing and contradictory state of affairs. Nor could it have been lost on him what contextual power the shambolic urban environments of Borodyanka, Hostomel, and Horenka — towns literally torn apart by war — could grant even murals humorously spray-painted upon its surfaces.

At the end of the video, Akers notes, “a heated local man points to an image the artist painted on a graffitied wall so that a pre-existing tag of a penis became a warhead atop an armored truck and declares, ‘For this, I would kick out all his teeth and break his legs.’ ” Even in a war zone, everybody’s a critic.

Related content:
The Making of Modern Ukraine: A Free Online Course from Yale Professor Timothy Snyder
Banksy Debuts His COVID-19 Art Project: Good to See That He Has TP at Home
Banksy Paints a Grim Holiday Mural: Season’s Greetings to All
How Ukraine’s Works of Art Are Being Saved in Wartime — Using the Lessons of World War II
Why Russia Invaded Ukraine: A Useful Primer
Based in Seoul, Colin Marshall writes and broadcasts on cities, language, and culture. His projects include the Substack newsletter Books on Cities, the book The Stateless City: a Walk through 21st-Century Los Angeles and the video series The City in Cinema. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on Facebook.