If you picked up The Original of Laura, Vladimir Nabokov’s final novel, you’ll have seen his distinctive index card-based writing method in action. Having died in 1977, Nabokov never completed the book, and so all Penguin had to publish decades later came to, as the subtitle indicates, A Novel in Fragments. These “fragments” he wrote on 138 cards, and the book as published includes full-color reproductions that you can actually tear out and organize — and re-organize — for yourself, “complete with smudges, cross-outs, words scrawled out in Russian and French (he was trilingual) and annotated notes to himself about titles of chapters and key points he wants to make about his characters.” That comes from a post by Dominic Basulto at Big Think, who highlights cards with “a full-on discussion of the precise word that Nabokov would like to describe a female character (fille, in French) and how best to render that word in English, while keeping the connotations and meaning of the word in French.” Reviewing The Original of Laura, Alexander Theroux describes the cards as a “portable strategy that allowed [Nabokov] to compose in the car while his wife drove the devoted lepidopterist on butterfly expeditions.”
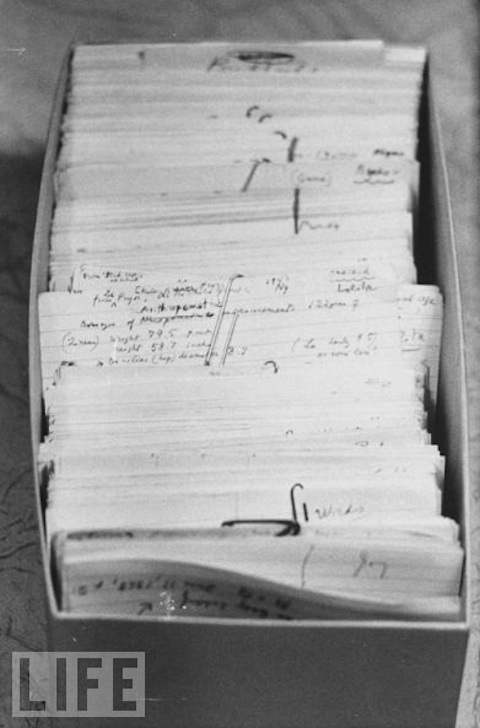

Nabokov could thus, between thoughts of his winged objects of interest, use the cards for “inserting words, writing memos to himself, scribbling afterthoughts: ‘invent tradename [for a medicine], e.g., cephalopium.’ ” They also served him earlier in his career; at the Library of Congress’ site for its Manuscript Division’s Nabokov collection, you can see a couple of the cards on which he wrote his best-known novel, 1955’s Lolita. Asked about his working methods by Herbert Gold in the Paris Review, he described the method forthrightly: “The pattern of the thing precedes the thing. I fill in the gaps of the crossword at any spot I happen to choose. These bits I write on index cards until the novel is done. My schedule is flexible, but I am rather particular about my instruments: lined Bristol cards and well sharpened, not too hard, pencils capped with erasers.” For every craft, the proper tool, and Nabokov remains, fragmentary last book and all, one of western literature’s most respected craftsmen of language — or, rather, languages, plural.
Note: You can download essential works by Vladimir Nabokov as free audiobooks (including Jeremy Irons reading Lolita) if you sign up for a free 30 Trial with Audible. Find more information on that program here.
Related Content:
Vladimir Nabokov Marvels Over Different Lolita Book Covers
Vladimir Nabokov (Channelled by Christopher Plummer) Teaches Kafka at Cornell
Alfred Hitchcock and Vladimir Nabokov Trade Letters and Ideas for a Film Collaboration (1964)
Nabokov Reads Lolita, Names the Great Books of the 20th Century
Vladimir Nabokov’s Delightful Butterfly Drawings
Colin Marshall hosts and produces Notebook on Cities and Culture and writes essays on cities, Asia, film, literature, and aesthetics. He’s at work on a book about Los Angeles, A Los Angeles Primer. Follow him on Twitter at @colinmarshall or on his brand new Facebook page.