The consolidation of big media in print, TV, and internet has had some seriously deleterious effects on politics and culture, not least of which has been the major dependence on social media as a means of mass communication. While these platforms give space to voices we may not otherwise hear, they also flatten and monetize communication, spread abuse and disinformation, force the use of one-size-fits-all tools, and create the illusion of an open, democratic forum that obscures the gross inequities of real life.

Today’s media landscape stands in stark contrast to that of the mid-to-late twentieth century, when independent and alternative presses flourished, disseminating art, poetry, and radical politics, and offering custom platforms for marginalized communities and dissenters. While the future of independent media seems, today, unclear at best, a look back at the indie presses of decades past may show a way forward.

Paradoxically, the same technology that threatens to impose a global monoculture also enables us to archive and share thousands of unique artifacts from more heterodox ages of communication. One stellar example of such an archive, Independent Voices—“an open access collection of an alternative press”—stores several hundred digitized copies of periodicals “produced by feminists, dissident GIs, campus radicals, Native Americans, anti-war activists, Black Power advocates, Hispanics, LGBT activists, the extreme right-wing press and alternative literary magazines during the latter half of the 20th century.”
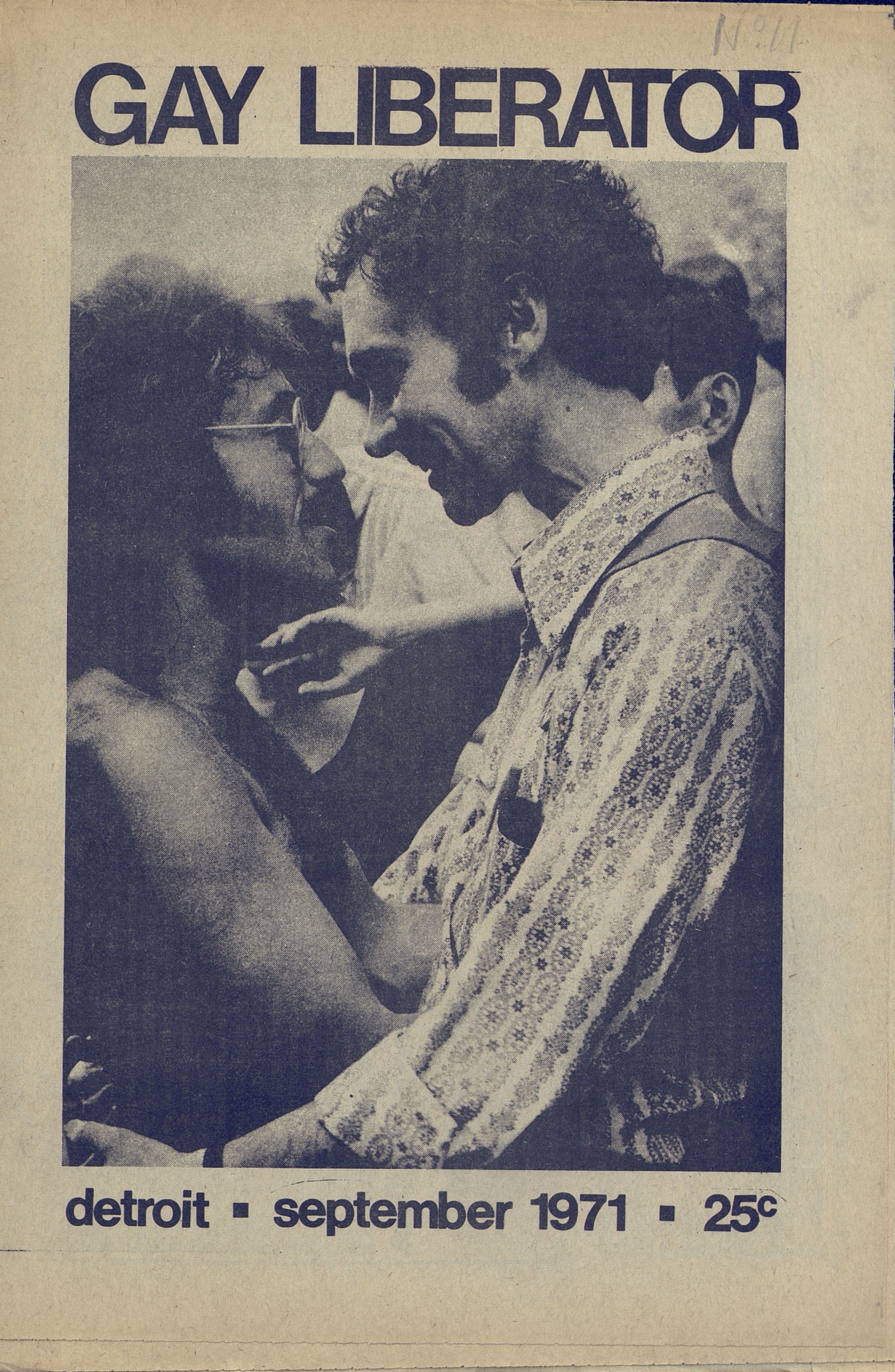
These publications come from the special collections of several dozen libraries and individuals and span the years 1951 to 2016. While examples from recent years show that alternative print publications haven’t disappeared, the richest, most historically resonant examples tend to come from the 60s and 70s, when the various strains of the counterculture formed collective movements and aesthetics, often powered by easy-to-use mimeograph machines.

As Georgia State University historian John McMillian says, the “hundreds of radical underground newspapers” that proliferated during the Vietnam war “educated and politicized young people, helped to shore up activist communities, and were the movement’s primary means of internal communication.” These publications, notes The New Yorker’s Louis Menand, represent “one of the most spontaneous and aggressive growths in publishing history.”

With publications from the era like And Ain’t I a Woman, Bread & Roses, Black Dialogue, Gay Liberator, Grunt Free Press, Native Movement, and The Yipster Times, Independent Voices showcases the height of countercultural activist publishing. These are only a smattering of titles on offer. Each issue is archived in a high-resolution, downloadable PDF, perfect for brushing up on your general knowledge of second-wave feminism or 60s Black Power; sourcing scholarship on the development of radical, alternative press over the past sixty years; or finding material to inspire the future of indie media, whatever form it happens to take. Enter the Independent Voices archive here.

Related Content:
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness